[CQE] 품질 관리 시스템
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
1. Planning
1) Strategic Planning
Strategic thinking starts with the CEO of the company. He/She must have a “Vision” for the company. The CEO and top management must decide what they want their company to look like at some point in the future. Some of the variables, that comprise strategic thinking include
- Current products, Employee abilities, Markets, Suppliers,
Market segments(부분), R&D, Facilities, The environment
2) Organizational Performance Goals
- The organizational performs many useful functions for its stakeholders. The term, stakeholder is a term recently used to describe parties or groups that have an interest in the welfare and operation of the company.
- Organizational performance and the related strategic goals may be determined for
* Short-term or long-term emphasis
* Profit
* Cycle times
* Marketplace response
* Resources
3) Organizational Performance Goals
- A company mission statement will address how the company will realize its vision and strategic goals
- A departmental mission statement concisely states how the strategic quality goals(and needs) of the organization will be implemented
4) Quality Principles
5) Quality Policies (CEO)
- Quality policies are often developed by top management in order to link together policies among all departments
6) Strategic and Tactical Quality goal
7) The Quality Department Role
- The quality department has a basic function in the organization : to coordinate the quality efforts
- Purchasing, production, engineering, manufacturing, marketing, vendor, suppliers and related staffs have to work together to meet the quality requirements
8) The Quality Plan
- For total quality to succeed, a structured process should be used. According to Juran, the process should include
* Establish a Quality Council (Quality Steering Committee)
- This quality council is a steering committee for the quality movement. The quality council has the responsibility for the growth, control, and effectiveness of total quality(TQ), as well as the incorporation of TQ into the strategic business plan
* Quality policies
* Strategic quality goals
* Deployment of quality goals
* Resources for control
* Measurement of performance
* Quality audits
2.DEPLOYMENT
1) Stakeholder Identification
- Businesses have many stakeholders including stockholders, customers, suppliers, management, employees (and their families), the community, and society.
- Each stakeholder has unique relationships with business.
- The SIPOC model explains the classic Supplier – Inputs – Processes – Outputs – Customer relationship
2) Performance Measurement
- Performance goals and corresponding measurements are often established in the areas of ; Profit , Marketplace response , Cycle times , Resources
3. Benchmarking
- Benchmarking is the process of comparing the current project, methods or processes
with the best practices and using this information to drive improvement of overall
company performance
1) Process Benchmarking
- Process benchmarking focuses on discrete work processes and operating systems
2) Performance Benchmarking
- This form of benchmarking usually focuses on elements of price, technical quality, ancillary product or service features, speed, reliability and other performance characteristics
3) Project Benchmarking
4) Strategic Benchmarking
- It moves across industries seeking to identify the winning strategies that have enabled
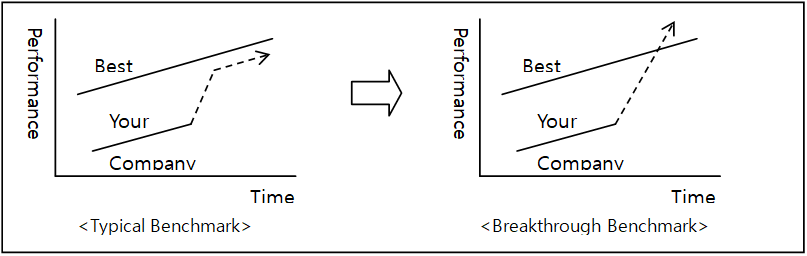
5) Benchmarking Sequences
- Determine current practices
- Identify best practices
- Analyze best practices
- Model best practices
- Repeat the cycle
4. Project Management
- Planning , Scheduling , Controlling
1) Time Lines
- The project time line is the most visible yardstick for management of project performance
- Tasks within the project are assigned starting and ending times
2) Resources
- Allocation of resources is part of the planning process
- While monitoring both time and resource use during the project is important
3) Methodology
- Manual project management methods (Advantages / Disadvantages)
- Computer/automated project management methods (Advantages / Disadvantages)
- One of the most widely used techniques in project management is network planning
- Common applications of network planning include the Program Evaluation and Review Technique(PERT),
the Critical Path Method(CPM) and Gantt charts
4) Program Evaluation and Review Technique(PERT)
- The critical path(주공정, 최장경로의 소요시간) and slack times(여유시간) for the project are calculated
- S = TL - TE (TL : 가장 늦은 완료일 , TE : 가장 빠른 예정일)
- Critical path : TL = TE AND S=0 , S > 0 자원과잉 , S < 0 자원부족
- Slack times (여유시간) : 최종 완료일을 변경하지 않는 범위내에서 각 단계에서 허용할 수 있는 시간
- Event : 활동이 개시 또는 완료되는 시점
- 단계(Event , ○) 중심의 확률적 모델전개, 최단기간에 목표달성 의도, 비용고려 않함
- 열거법 , 전진/후진 계산법
5) Critical Path Method(CPM)
- The critical Path Method(CPM) is very similar PERT, except PERT is event oriented , while CPM is activity oriented
- Unique feature of CPM include
* The emphasis is on activities
* The time and cost factors for each activity are considered
* Only activities on the critical path are contemplated
* Activities with the lowest crash cost (per incremental time savings) are selected first
* As an activity is crashed, it is possible for a new critical path to develop
# Crash : 추가비용을 투입해서 일정단축(Critical path에 속해있는 Activity중에 비용이 가장 저렴한 Activity부터 진행)
- 활동(Activity, →) 중심의 확정적 모델전개, 목표기일 단축과 비용의 최소화, 비용고려
6) Gantt Charts (Bar charts)
- They do not show interdependencies of activities (Disadvantage)
- The network relationship between activities which are indicated in PERT and CPM charts,
are not shown on the Gantt chart
- Milestone 실행단계에서 효과적으로 사용